Are you scouring the internet for 'hydrothermal vents chemosynthesis'? You will find questions and answers on the subject here.
Table of contents
- Hydrothermal vents chemosynthesis in 2021
- Chemosynthetic bacteria
- Chemosynthetic organisms
- Hydrothermal vents animals
- Chemosynthesis process
- Hydrothermal vents life
- Importance of hydrothermal vents
- Hydrothermal vents facts
Hydrothermal vents chemosynthesis in 2021
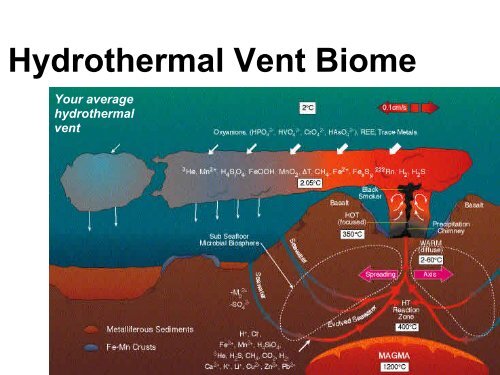 This picture representes hydrothermal vents chemosynthesis.
This picture representes hydrothermal vents chemosynthesis.
Chemosynthetic bacteria
 This image demonstrates Chemosynthetic bacteria.
This image demonstrates Chemosynthetic bacteria.
Chemosynthetic organisms
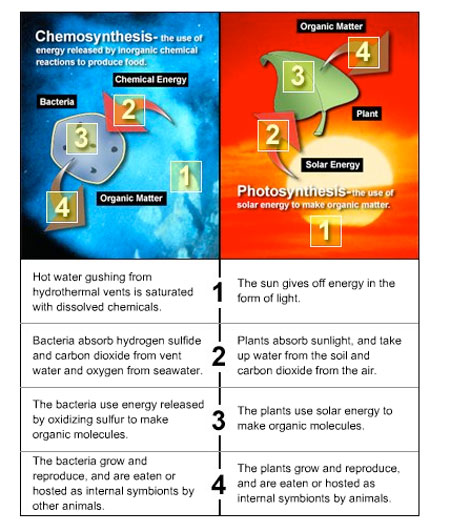 This image representes Chemosynthetic organisms.
This image representes Chemosynthetic organisms.
Hydrothermal vents animals
 This image shows Hydrothermal vents animals.
This image shows Hydrothermal vents animals.
Chemosynthesis process
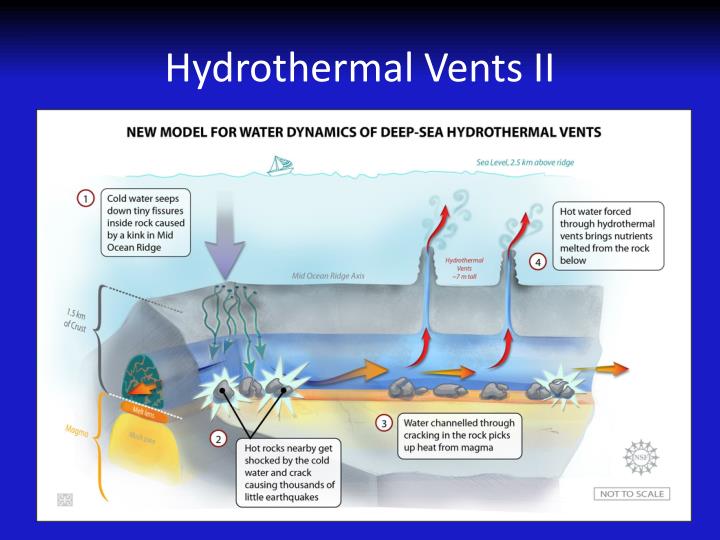 This picture shows Chemosynthesis process.
This picture shows Chemosynthesis process.
Hydrothermal vents life
 This image representes Hydrothermal vents life.
This image representes Hydrothermal vents life.
Importance of hydrothermal vents
 This image representes Importance of hydrothermal vents.
This image representes Importance of hydrothermal vents.
Hydrothermal vents facts
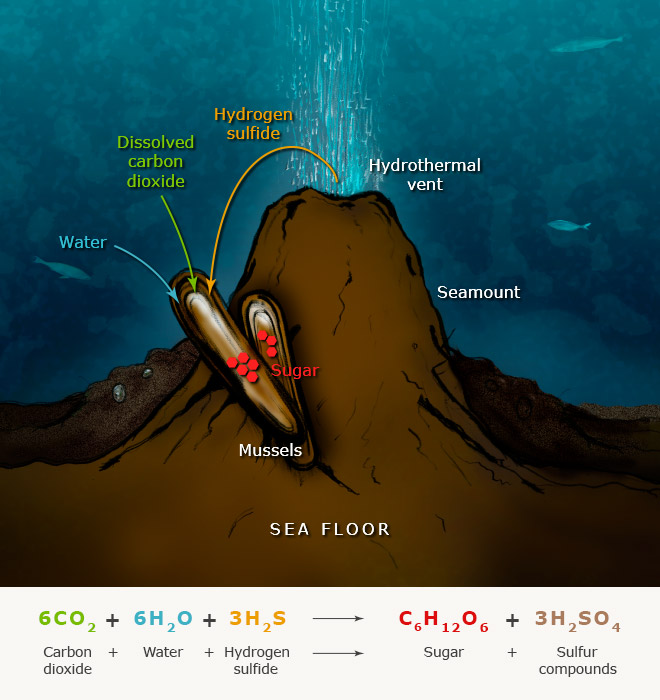 This picture shows Hydrothermal vents facts.
This picture shows Hydrothermal vents facts.
How long does it take for a hydrothermal vent to close?
The hydrothermal vents—the source of life-sustaining chemicals—can be extinguished at any time by earthquakes, lava flows, or rock falls. Many vents close after a few months or years, and few seem to survive more than a couple of decades.
What makes a hydrothermal vent a chemosynthetic based ecosystem?
The hydrothermal vents are recognized as a type of chemosynthetic based ecosystems (CBE) where primary productivity is fuelled by chemical compounds as energy sources instead of light (chemoautotrophy). Hydrothermal vent communities are able to sustain such vast amounts of life because vent organisms depend on chemosynthetic bacteria for food.
How are hydrothermal vents used in the ocean?
Scientists later realized that bacteria were converting the toxic vent minerals into usable forms of energy through a process called chemosynthesis, providing food for other vent organisms. Hydrothermal vents are like geysers, or hot springs, on the ocean floor.
Where does chemosynthesis take place in the sea?
The most extensive ecosystem based on chemosynthesis lives around undersea hot springs. At these hydrothermal vents, a chemical-rich soup bubbles out of the crust and into the bottom of the sea. Boiling hot, saturated with toxic chemicals and heavy metals, and more acidic than vinegar, vent waters are deadly to most marine animals.
Last Update: Oct 2021